Test Plan is a document providing structural approach describing how testing will be accomplished in the Project. This acts as a contract between testing team and stakeholders on how testing is planned for the project.
For successful execution of
testing in the project, it is very important to do thorough planning of the
testing requirement and documenting the same in the form of test plan.
Most of the organisation have defined template for test plan
and have slight difference in the structure of the test Plan from each other. What information needs to be captured in the test plan will be discussed in
this article in the first section:
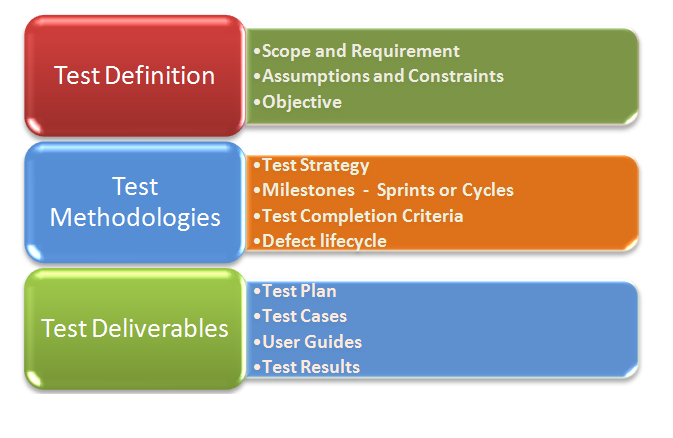
- Defining
the Scope of testing – The first and one of the important component in test
planning is defining the scope of testing and at the same time providing the
items which are Out of scope of testing. Scope of testing should be in line
with the overall scope of Project. Defining scope early in testing helps in
defining the acceptance criteria and agrees on the exit criteria for testing.
- Objective of Testing in the Project should be defined - Objective of testing can be testing the functional requirement or creating an automation suite for regression scope. Also there can be multiple objective of testing with some critical and some secondary objective e.g. : Testing complete functional requirement of application can be primary objective of testing with communicating all known defects and issue with different stakeholder and closure on all of them before release to production can be the secondary objective of testing. All the objectives should be clearly defined in test plan. Each objective should have the priority defined and acceptance criteria should be associated with each test objective.
- Staffing and training needs for the testing team should be mentioned in the test plan.
- Environment and resource requirement required for testing, i.e. Software and hardware requirements should be clearly defined.
- Assumptions acts as probable risks to Project. All the assumptions should be added in test plan and proper sign-off should be taken from stakeholders to keep them informed and confirmation should be taken from them for the correctness of assumptions made during testing and will not lead to possible risks in future.
- We should define constraints in the test plan. Constraints impact the efficiency and effectiveness of testing. Constraint can include for e.g. staffing, time or cost constraints
To summarize, so far we have discussed the ‘What’ part of testing, i.e. What we will test, what will be our scope, what our assumption, constraints are, what will be the scope of testing. Once we are clear on What, Next question is how to do what.
How Testing will be executed is explained in Testing
Methodology. The Key points explained in Testing Methodology include:
- Define testing strategies for
different phases and functional and non-functional requirements. This includes:
- Different types of testing required for requirement.
- Approach for each testing type, e.g. Regression, functional, automation or locale testing.
- Risk/issues identification and test data generation for testing types.
- Testing cycle for each testing and testing milestones are set.
- Entry and exit criteria for each testing milestones are described
- Providing defect lifecycle to be followed.
- Defining testing schedule in sync with the milestone defined.
Another Topic to be
covered in test plan includes test deliverables and defining the exit criteria
for testing completion. Test deliverables should be defined; it can include
user guide, test scripts, test data, Test execution results, and Test plan.
Together, we can add
matrix for different areas in test plan for easier understanding and better
explanation. We will discuss on methodology and test deliverables in details in
the next articles on topic Software Testing.